A Hybrid ANN-SNN Architecture for Low-Power and Low-Latency Visual Perception
Jun 17, 2024·
,
,
,
·
1 min read
Asude Aydin
Mathias Gehrig
Daniel Gehrig
Davide Scaramuzza
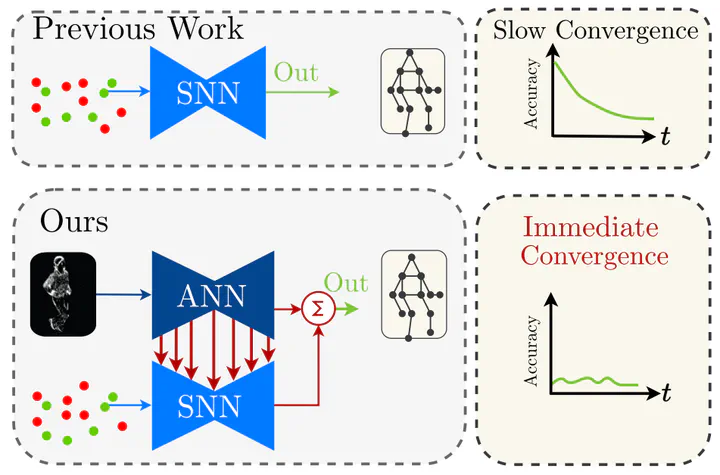
Abstract
Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are a class of bioinspired neural networks that promise to bring low-power and low-latency inference to edge-devices through the use of asynchronous and sparse processing. However, being temporal models, SNNs depend heavily on expressive states to generate predictions on par with classical artificial neural networks (ANNs). These states converge only after long transient time periods, and quickly decay in the absence of input data, leading to higher latency, power consumption, and lower accuracy. In this work, we address this issue by initializing the state with an auxiliary ANN running at a low rate. The SNN then uses the state to generate predictions with high temporal resolution until the next initialization phase. Our hybrid ANN-SNN model thus combines the best of both worlds. It does not suffer from long state transients and state decay thanks to the ANN, and can generate predictions with high temporal resolution, low latency, and low power thanks to the SNN. We show for the task of eventbased 2D and 3D human pose estimation that our method consumes 88% less power with only a 4% decrease in performance compared to its fully ANN counterparts when run at the same inference rate. Moreover, when compared to SNNs, our method achieves a 74% lower error. This research thus provides a new understanding of how ANNs and SNNs can be used to maximize their respective benefits.
Type
Publication
IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)
The work by Asude Aydin that contributed to the paper “A Hybrid ANN-SNN Architecture for Low-Power and Low-Latency Visual Perception” at a CVPR Workshop 2024 lead to a UZH Master Thesis Award.